How Do Thermal Imaging Cameras Work?
What is a Thermal Imaging Camera?
A thermal imaging camera creates a digital image of an environment by mapping the temperature of whatever is in its view. Every object and surface has a heat signature, created by the energy it transmits, known as infrared energy.
A thermal imaging camera detects the infrared data and converts it into an electronic image with colours indicating temperature variation. It is a non-contact and often handheld temperature-sensing device detecting and displaying object temperature as images.
So, how does a thermal imaging camera work?
How Do Thermal Cameras Work?
To understand how thermal imaging cameras work, disregard everything you know about how photography cameras produce images. They have nothing to do with light bouncing off solid surfaces, in fact, thermal cameras can work in complete darkness.
Heat and light are both parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. However, thermal imaging cameras produce images and video from heat energy, as opposed to visible light. This thermal or ‘infrared’ energy can’t be detected by a regular camera, much like how infrared cameras can’t detect and capture light levels.
The inner workings of a thermographic camera consists of a sensor array that contains thousands of pixels arranged in a grid, which reacts to infrared energy. The focused infrared energy produces an electronic signal to which the camera processor assigns a colour.
Each temperature value has a different colour, which when mapped produces the thermal image of an object or environment.
At Process Parameters, we’re a UK distributor of Optris thermal cameras. Contact our team to discuss your application and find out how thermal imaging can improve your process.
Send An EnquiryA Brief History of Thermographic Cameras
In 1800, England-based German astronomer, musician and composer William Herschel discovered the infrared spectrum. Herschel named this discovery the ‘thermometrical spectrum’, occasionally referring to it as ‘the invisible rays”. It wasn’t until the early 1900s that it started being referred to as infrared.
Herschel’s discovery of the infrared spectrum is the basis for modern thermal imaging cameras. It led to many innovations in the field of infrared technology, including the development of the first infrared camera in 1929, a motion camera used by the British army.
Since then, thermal imaging cameras have been used in a variety of fields, including medical, industrial, scientific, and security. They are now widely used in many applications, offering superior performance in dark and low-light conditions.
What Can Thermal Imaging Detect?
Thermal imaging cameras detect infrared heat, which is invisible to the naked eye. All objects give off thermal energy, and the hotter the object the more energy is produced. Think about hovering your hand over a stove to check if it’s been on recently, the heat we can feel in the air is infrared radiation.
Thermal imagers use sensor arrays to detect this heat energy and produce shapes and accurate mappings of heat distribution.
What Can a Thermal Imaging Camera See Through?
All infrared cameras will see the first solid or liquid surface which can include vapour and particles, meaning technically it can’t see through anything. However, it is still sometimes the most effective camera technology for ‘seeing through’ thin plastic, fog, smoke, foliage, dust, fog, rain, sand, snow and darkness.
The displayed images may not be perfect, but in most of these cases, they will produce a clearer image than a visible light camera. For things like search and rescue the image is good enough to detect a person hiding in the undergrowth, but for actual temperature measurement, it’s likely to be inaccurate.
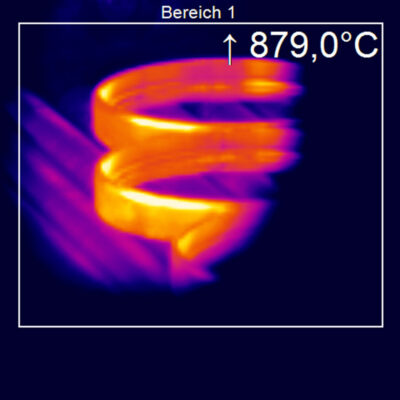
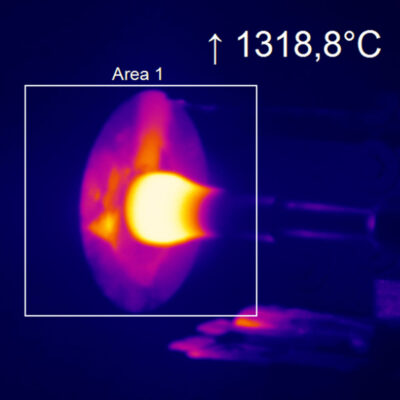
What Makes Thermal Imaging Cameras Useful?
Thermal imaging cameras are incredibly useful because they can detect infrared radiation emitted by all objects, regardless of lighting conditions. This makes them highly reliable and efficient, as they can detect heat sources and identify targets in the dark.
Additionally, they are 100% non-invasive, meaning they detect infrared energy emitted from the surface of the subjects without needing any physical contact. They also detect minuscule differences in heat – as small as 0.04°C, and extremely high-tech (and expensive) systems as little as 0.01C.
What are the Limitations of Thermal Imaging Cameras?
Although heat sensing cameras can see shapes and forms undetectable to the human eye, they’re not without their limitations.
Glass
Contrary to what you might expect, pointing a thermal imaging camera at a piece of glass at ambient temperature will produce an image of yourself instead of what’s on the other side. This is because glass is highly reflective, stopping the transmission of infrared radiation.
However, at Process Parameters, we can use our cameras very effectively to measure the temperature of glass at high temperatures in manufacturing environments. Using our metal cameras (1M, 08M, and 05M) we can see through ordinary quartz-based glass.
Metal
Metal performs in the same way as glass, giving you an image of yourself rather than what you’re trying to capture. Thermal cameras will never be able to see through metal but can detect hot and cold spots on the inside of a metal object or structure.
Fog
The water droplets from fog and rain can severely limit the temperature measurement capabilities of thermal cameras due to the scattering of radiation. However, when it comes to producing an image, thermal cameras may still perform better in foggy conditions than the human eye or even a visible light camera.
What is a Thermal Imaging Camera Used For?
Thermal imaging cameras are invaluable for emergency services. From night vision detection during police chases, to search and rescue missions, to firefighters locating survivors in smoke, many incidents could have much more sombre outcomes without thermal camera technology.
In manufacturing, thermal imaging can detect liquid levels in opaque containers, detect hot and cold spots to prevent risk and damage, and improve quality control processes.
For challenging environments, industrial usage may require thermal cameras to meet official regulations for manufacturing standards in the UK. This applies to explosive gases, mining, and applications with high volumes of dust such as grain handling.
Process Parameters’ Thermal Imaging Cameras
All of our infrared cameras are designed for fixed installations and are used to measure temperature accurately. We don’t typically sell into the search and rescue or security industries as the products used to produce images are of a lower required specification than our technology.
We do however sell into industrial applications encompassing research and development, (machine or product developments), condition monitoring (checking equipment is operating properly) and quality control.
We have a variety of cameras. Some for general-purpose applications, some for Glass and others for Metals. Another key customer is those requiring fire detection and prevention, as with our cameras a high temperature can be detected before a fire starts.
Our team here at Process Parameters will be able to assist you with certification requirements for industrial infrared camera usage.
Other uses for thermal cameras include drones, wildlife photography, wildlife tracking, environmental monitoring, airport security, marine traffic monitoring, military applications, building inspections and monitoring patient health.
See Our Thermal CamerasWhat to Consider When Choosing a Heat-Sensing Camera
Choosing a particular heat detection product can feel like a complex decision. All the available varieties, price differences, designs, and sensitivities can make it difficult to know what is truly the best option for your application.
- What is your budget?
- Do you need to meet any UK, EU or other standards and certifications?
- Design – aesthetic and ergonomic
- What are the ideal size and weight?
- What are your requirements in terms of thermal range, lens interchangeability, hardware and software calibration, image resolution and screen resolution if applicable?
For more information on any thermal imagers, or for further advice, please contact one of our support team who will be happy to assist you.
Send An Enquiry
Summary of How Do Thermal Cameras Work?
We hope you found this article on ‘how does a thermal imaging camera work?’ useful.
Process Parameters is the UK distributor for Optris, a manufacturer of infrared thermometers and thermal imaging cameras. Contact our team to discuss your application and find out how thermal imaging can improve your process.
For further information please email sales@processparameters.co.uk or call 01628 778788.
Send An EnquiryGeneral Purpose IR Thermometers
General Purpose IR Thermometers
General Purpose IR Thermometers
FAQs
How do thermal cameras measure temperature?
Infrared light, invisible to the human eye, is emitted by various objects as heat energy. Thermal imaging devices, first recognised by Sir William Herschel, detect this infrared radiation. By capturing infrared rays and converting them into electrical signals, these cameras create a visual picture where different colours represent temperature differences, indicating heat loss or potential problems in electrical systems or HVAC equipment.
Is an infrared camera the same as a thermal camera?
Yes, an infrared camera is essentially the same as a thermal camera. Both devices detect infrared energy, also known as thermal energy, emitted by objects. They capture infrared rays from the target area and convert them into a resulting image, or infrared photography, where colours represent the temperature of the object, making them interchangeable terms in many contexts, including military uses.
Who would use a thermal imaging camera?
Thermal imaging cameras are invaluable tools for various professionals. Emergency services like firefighters, search and rescue teams, and police use them for finding people in difficult conditions. Additionally, medical professionals, building maintenance workers, gas and electrical workers, and wildlife researchers rely on these cameras for tasks such as detecting heat loss, inspecting electrical systems, and conducting non-invasive animal studies, even in low ambient light.
How far can a thermal camera detect?
The detection range of a thermal camera depends on its sensitivity and the environmental conditions. While there’s no strict limit, clear nights allow these cameras to detect distant objects like the moon and stars. However, obstacles like water droplets from rain or fog can obscure the view, limiting the camera’s effective range. The resulting image will include all visible surfaces or objects within the camera’s field of view.
Do thermal cameras work underwater?
No, thermal cameras do not work effectively underwater. Water does not transmit infrared energy well, acting as a barrier to infrared radiation. This makes thermal imaging cameras unsuitable for underwater use, as the water itself becomes an opaque structure, preventing accurate heat detection.
Do thermal cameras work through glass?
No. Glass is highly reflective and does not allow thermal radiation to pass through it, stopping the ability of thermal cameras.
Can thermal imaging cameras see through walls?
Thermal cameras cannot see through solid walls or concrete. However, they can detect temperature differences on the surface of walls, indicating hot or cold spots within, such as pipes carrying hot or cold water. This capability allows thermal cameras to identify potential issues like heat loss or electrical resistance behind walls without actually seeing through them.
How does thermal work?
Thermal energy works by transferring heat from a warmer object to a cooler one, seeking thermal equilibrium. This natural process follows the principle that heat flows from regions of higher temperature to lower temperature until a balanced state is achieved, making it a fundamental aspect of various scientific and industrial applications.
How does an infrared camera work?
An infrared camera works by detecting infrared radiation emitted or reflected by objects. It uses an infrared sensor to capture the radiation and then converts it into a visual image, allowing us to see and interpret temperature variations in the scene.
Related Articles:
- 5 Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras
- Can a Thermal Camera See Through Walls?
- How to Use an Infrared Thermometer
- How Does an Infrared Thermometer Work?
- Choosing an Infrared Pyrometer
- What is an Infrared Thermometer?
- Why is a Pin Sharp Thermal Image Important?
- How Can a Thermal Imaging Camera Become Part of Your Process?
- Can You Improve Your Thermal Efficiency With Imaging Cameras?
- What is Optical Resolution?
- What is a Line Scan Camera?
- Use of Temperature Sensors in Glass Manufacturing Process





