Industrial Thermal imaging cameras
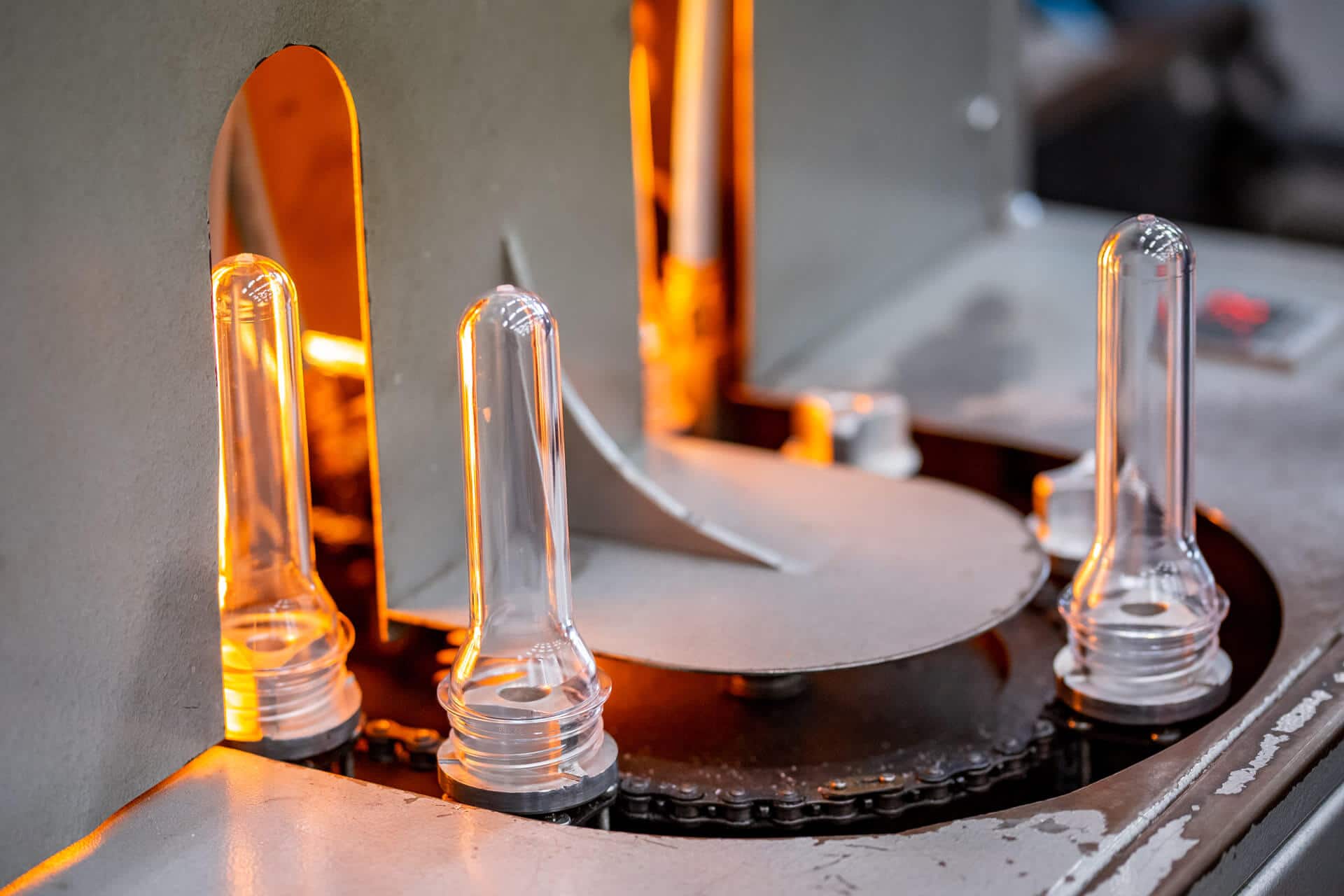
Thermal imaging cameras are widely used for industrial purposes. Unlike handheld infrared thermometers, high-end thermal imaging cameras are versatile tools that boost safety and precision, even in high-speed applications, thus helping industry experts work smarter.
That said, the importance of successfully driving energy efficiency while slashing operational costs of various industrial manufacturing processes has become critical. By enabling automated non-contact maintenance and monitoring of product temperatures, a thermal camera can help drastically improve energy efficiency.
Let’s look into how modern industries leverage thermal imaging for energy efficiency and improve operational efficacy:

How Does a Thermal Imaging Camera Work?
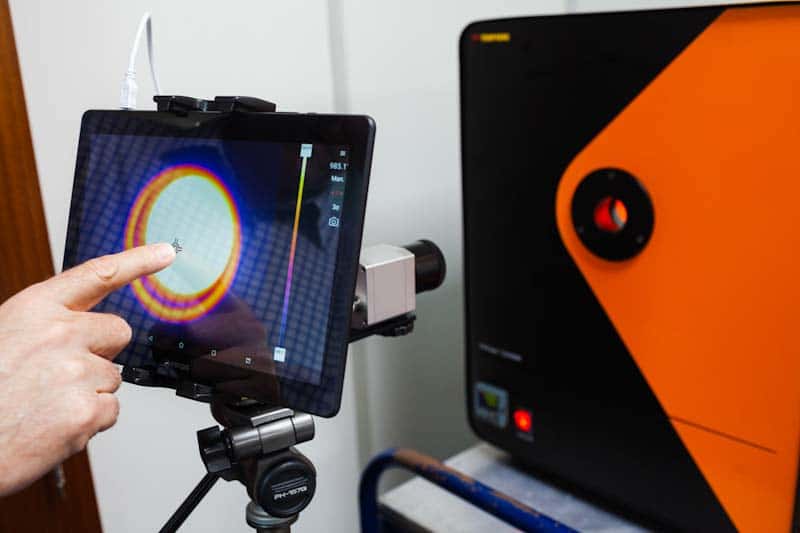
A thermal or infrared (IR) imaging camera is a non-contact device that detects and measures the infrared energy (in other words, heat signature) radiated by an object being analysed.
Later, it turns the captured infrared data into a thermal image.
Read more about ‘How Thermal Imaging Cameras Work‘ here.
A thermal imager comprises an optical system that directs infrared heat emitted by an object onto a sensor array.
This sensor array includes thousands of detector pixels placed in a grid that turns the infrared signal focused on them into an electronic signal.
The camera processor then picks up the electric signals given off by the pixels and produces a colour map of the apparent temperature of the object using a high-end mathematical algorithm. Each temperature value depicts a distinct colour. The final colour matrix is fed to the device memory as well as the display that shows the thermal image of that object.