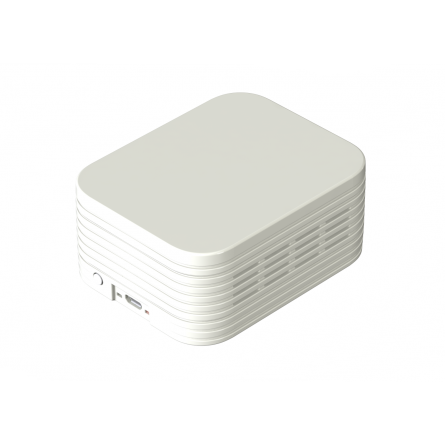
NSnappy Hub 4G LWEU LoRaWAN Base Station
The NSnappy Hub LoRaWAN base station gathers data from wireless IoT devices and sends it to the NSnappy service. It provides various internet connections (4G, Wi-Fi, Ethernet) in one device and is ideal for data transfer within the mobile network coverage.
Technical Details
- Storage: -40…+85 °C, relative humidity 0-95%, non-condensing
- Operating conditions: -40…+60 °C, relative humidity 0-95%, non-condensing
- Protection Class: IP65
- Case Material: Plastic
- Dimensions: 180 x 110 x 56.5 mm
- Installation: Desktop, wall or pole mounting
Prices from £510.00
NSnappy Hub LoRaWAN Base Station
The NSnappy Hub LoRaWAN base station gathers measurement data from wireless IoT devices and transmits it to the NSnappy service. It provides multiple internet connections (4G, Wi-Fi, Ethernet) in a single device and is suitable for data transfer within mobile network coverage. The product is available for purchase with or without a SIM card.
Key benefits include:
- All major internet connections in one device
- Sleek, robust, and splash-resistant housing
- Simple and rapid installation and operation
The NSnappy Hub LoRaWAN base station is designed to operate in a wide range of conditions, with a storage temperature range of -40 to +85 °C and IP65 protection. It features dimensions of 180 x 110 x 56.5 mm and can be easily installed on a desktop, wall, or pole, with wall mounting accessories provided.
The user interface includes a reset button, 2 x Type-C console ports, and front panel LEDs for POWER, STATUS, LoRa, Wi-Fi, LTE, and ETH. Additionally, it is equipped with built-in features such as Watchdog, RTC, and Timer. The LoRaWAN protocol complies with standards V1.0 Class A/Class B/Class and V1.0.2 Class A/Class B/Class C, with 2 internal antennas and support for 8 channels.
The Ethernet port supports PoE Power Delivery and operates at 10/100/1000 Base-T, while the internal WiFi antenna supports IEEE 802.11 b/g/n standards at 2.4GHz, with options for AP or Client settings and WPA/WPA2 authentication.
Specifications of The LoRaWAN Base Station
General
- Storage: -40…+85 °C, relative humidity 0-95%, non-condensing
- Operating conditions: -40…+60 °C, relative humidity 0-95%, non-condensing
- Protection class: IP65
- Case Material: Plastic
Dimensions
- Dimensions: 180 x 110 x 56.5 mm
- Installation: Desktop, wall or pole mounting, Wall mounting accessories are included in the product
User Interface
- Reset button: 1 x RST
- Console port: 2 x Type-C
- LEDs: Front panel: 1 × POWER, 1 × STATUS, 1 × LoRa, 1 × Wi-Fi, 1 × LTE, 1 × ETH
- Built-in: Watchdog, RTC, Timer
LoRaWAN
- Protocol: LoRaWAN standard, V1.0 Class A/Class B/Class, V1.0.2 Class A/Class B/Class C
- Antenna: 2 x internal antenna
- Channels: 8 (Half/full-duplex)
- Frequency: 863-870 MHz (LoRaWAN 1.0.2 EU band)
- Current: Max +27 dBm
- Sensitivity: -140 dBm @ 292 bps
Ethernet
- Port: 1 x RJ45 (PoE Power Delivery supported)
- Physical layer: 10/100/1000 Base-T (IEEE 802.3)
- Data transfer speed: 10/100/1000 Mbps (Auto-Sensing)
- Interface: Auto MDI/MDIX
- Settings: Full or Half Duplex (Auto-Sensing)
WiFi
- Antenna: Internal
- Standards: IEEE 802.11 b/g/n, 2.4GHz
- Settings: AP or Client
- Security: WPA/WPA2 authentication, WEP/TKIP/AES encryption
| Brand |
|---|
What is a Base Station?
A base station is a central communication hub that connects wireless devices to a network. It facilitates data transmission, reception, and routing for mobile phones, IoT devices, and other wireless technologies. Base stations are essential for establishing and maintaining wireless connections, enabling seamless communication and data transfer within a specific coverage area.What is a LoRaWAN Base Station?
A LoRaWAN base station is a device that collects and transmits data from low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) IoT devices using the LoRaWAN protocol. It facilitates long-range communication and enables connectivity for IoT devices, typically used in applications such as smart cities, agriculture, and industrial IoT.fzWhat is the Purpose of LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN serves the purpose of enabling efficient, long-range communication for low-power IoT devices. It provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for transmitting small packets of data over extended distances, making it suitable for applications such as smart cities, agriculture, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring where long battery life and broad coverage are essential.Is LoRaWAN Better Than Wi-Fi?
LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi serve different purposes, with each offering distinct advantages. LoRaWAN excels in long-range, low-power applications, making it ideal for IoT devices in remote or outdoor environments. Wi-Fi, on the other hand, provides higher data transfer speeds over shorter distances, making it more suitable for high-bandwidth applications within a confined area.Related products
4-20mA Temperature Transmitters
Universal Input Transmitter – Nokeval RMD680/RMD681 16/8 Channel
Our Nokeval Products
Our Nokeval Products
Our Nokeval Products
Our Nokeval Products
Nokeval Kube-Sky-RHT Wireless Temperature & Humidity Transmitter